| Operations | << | >> |
|---|
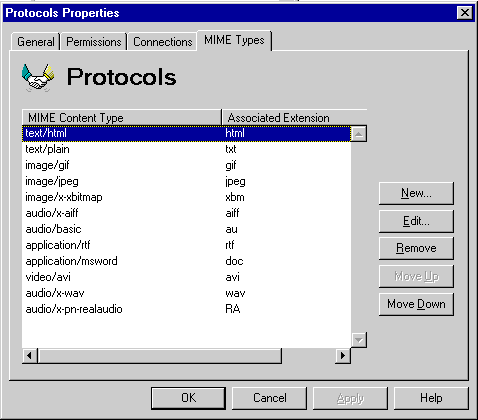
Microsoft Exchange Server can assign appropriate file extensions for inbound attachments if the Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) content type and corresponding file extensions are defined in the MIME Types property page. For example, you can specify that all attachments with a content type of text/HTML are automatically given an extension (such as .Htm). For outbound attachments, a MIME type is used for the file extensions listed in the MIME Types property page.
Note Duplicate entries are allowed for both the content type and the file extension. The first occurrence found in the list is the mapping that is used.

Use the MIME Types property page to add a new MIME type to the list.
In MIME, there are primary types, which describe the general content of a message, and subtypes, which further describe the specific data. The two types are separated by a forward slash (/), such as text/plain.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| MIME content type | Type the content for which you will associate an extension. Common types are text, application, multipart, image, audio, video, and message. |
| Associated extension | Type the extension that will be associated with the content type. Do not use a period before the extension. |
Use the MIME Types property page to remove a MIME type from the list.
Use the MIME Types property page to specify the order of the MIME content type in the list. The order of content types is important if the same content type maps to multiple extensions. For example, an item with a .Doc extension can be mapped to application/msword, application/binary, or text/plain. By specifying the processing order, you can ensure that the .Doc item is mapped to the correct content type. Content types are processed in order from first to last.