| Operations | << | >> |
|---|
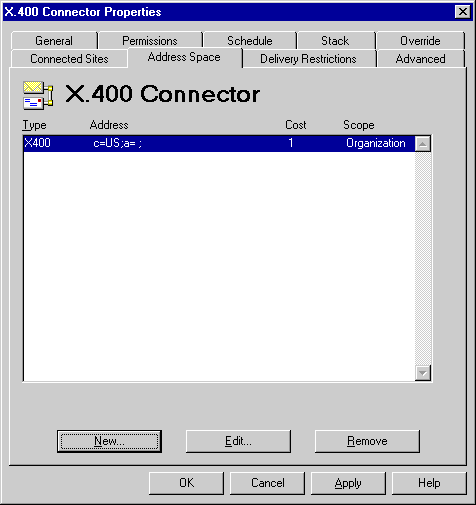
Use the Address Space property page to define the type and format of addresses used to identify messages to another site or foreign system. Each entry is called an address space and contains only as much of the address as is necessary to distinguish messages that should be sent through this connector. You need to configure only the necessary X.400 address space options to uniquely identify the route to the site or foreign system.
For example, if you want to use this connector to route only X.400 messages to a foreign system called Ferguson and Bardell (FAB), type the following in the Address Space property page:
Private Management Domain Name (p) = FABAdministrative Management Domain Name (a) = mciCountry (c) = us
The cost associated with each address space is used to optimize message routing to the foreign system but does not affect message reception. Lower cost address spaces take precedence over higher cost address spaces. If two or more routes are available with the same cost, the load placed on the routes is roughly equal. Routing costs range from 1 to 100.
Note The Connected Sites property page also contains address information, but is used only when connecting to other Microsoft Exchange Server sites.

Use the Address Space property page to create a new address or modify an existing address space.
Note An asterisk (*) can be used for a multicharacter wildcard in an address space. A percent symbol (%) can be used for a single character wildcard.
For more information about address spaces, see Chapter 4, "Address Spaces" or Microsoft Exchange Server Concepts and Planning.