 To implement this configuration
To implement this configuration| Migration | << | >> |
|---|
If you are performing a multiphase migration, you will also need to:
For information about synchronizing directories, see Microsoft Exchange Server Operations.
You can connect MS Mail (AppleTalk) servers with Microsoft Exchange Server computers using the MS Mail Connector. This connection allows you to:
To decide how to connect MS Mail (AppleTalk) sites to Microsoft Exchange Server sites, consider the following issues:
The following table summarizes the various options for connecting MS Mail (AppleTalk) and Microsoft Exchange Server computers.
| Network configuration | Connection options |
|---|---|
| MS Mail servers on same network as Microsoft Exchange Server. | Install a Microsoft Exchange Server MS Mail Connector. |
| MS Mail servers on network isolated from Microsoft Exchange Server. |
Connect a Microsoft Exchange Server computer in the MS Mail (AppleTalk) location to the main Microsoft Exchange Server computer through SMTP, RAS, X.25, or public X.400 connections. - or - Use an MS Mail (AppleTalk) 3.1d server in the Microsoft Exchange Server location as its own site, and connect the two MS Mail (AppleTalk) sites with AppleTalk Remote Access. - or - Use an MS Mail for PC Network postoffice in the MS Mail (AppleTalk) site, and use X.25 or asynchronous connections between the postoffice and the Microsoft Exchange Server connector postoffice. Connect the MS Mail (AppleTalk) server to the MS Mail (PC) postoffice with the Mail Connection Gateway, version 3.2. |
| MS Mail servers connected to an MS Mail (PC) postoffice with Mail Connection Gateway, version 3.2. |
Connect Microsoft Exchange Server to the MS Mail (PC) postoffices and backbone to MS Mail (AppleTalk) servers. - or - Remove the existing connection gateway and reinstall it to connect to the connector postoffice. Set the registry entry "SetResponsibleBit" to a value of 0 for the MSExchangeMSMI service after the gateway is installed. |
For more information about the MS Mail Connector, see Microsoft Exchange Server Operations.
Note If your users connect to MS Mail (PC) gateways with the MS Mail Connection Gateway version 3.2, they can continue to send and receive mail through these gateways after migrating.
MS Mail (AppleTalk) gateways are not compatible with Microsoft Exchange Server. If you want to maintain connectivity with these foreign systems, you need to do one of the following:
If inbound messages route through Microsoft Exchange Server, you also need to do the following:
After the native gateway is reestablished as a Microsoft Exchange Server gateway or connector, you can start migrating mailboxes. The following table summarizes the options. To minimize disruptions in mail delivery, the first option is the best.
| Configuration | Result |
|---|---|
| Mail to native gateway is redirected, and addresses of migrated users and custom recipients are updated. | All users receive mail sent to both new and old addresses. |
| Mail to native gateway is redirected, and only addresses of migrated users are updated. | Migrated mailboxes receive mail sent to both new and old addresses. Non-migrated mailboxes only receive mail sent to the new addresses; the mail sent to old addresses is returned to sender as non-deliverable. |
| Mail to native gateway is redirected, and no addresses are updated. | Users receive mail sent to their new addresses, but mail sent to old addresses is returned to the sender as non-deliverable. |
| Mail to native gateway is not redirected. | Migrated mailboxes must periodically connect to the MS Mail (AppleTalk) server to check for mail. Or you can use the Out of Office Server (server version) to periodically forward all mail from migrated mailboxes to the corresponding MS Mail (AppleTalk) custom recipient for the Microsoft Exchange Server mailbox. You then respond to the sender with the user's new address. The Out of Office Server is available only in MS Mail (AppleTalk), version 3.1d. |
Note When you redirect inbound mail to an MS Mail (PC) gateway, address mapping depends on the MS Mail (AppleTalk) server's postoffice address and gateway features.
When you migrate mailboxes to Microsoft Exchange Server, users can use Microsoft Exchange Server and MS Mail (PC) gateways. You can modify mailbox addresses to match old external addresses. To maintain external addresses, you must replace or supplement the default gateway address of the Microsoft Exchange Server custom recipient or mailbox. You will probably want to maintain the Internet (SMTP) addresses.
The following are sample configurations for maintaining addresses during coexistence and migration. In each configuration, MS Mail (AppleTalk) connects to MS Mail (PC) with the MS Mail Connector version 3.2 and receives mail addressed to hex@proxypo.proxynet.<domain>.
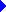
Sample Configuration No. 1 Microsoft Exchange Server connects to MS Mail (PC) and sees MS Mail (AppleTalk) mailbox addresses as MS Mail addresses. The directory synchronization server is either a Microsoft Exchange Server computer or a postoffice.
 To implement this configuration
To implement this configuration
Obj-class,common-name,target-address,when-createdobj-class,mode,common-name,secondary-proxy-addressFollow this procedure every week. Sort first on when-created, and delete all the old entries.
Sample Configuration No. 2 The Microsoft Exchange Server computer connects directly to MS Mail (AppleTalk) and MS Mail (PC) and is the directory synchronization server, importing MSA addresses from MS Mail (AppleTalk) and exporting MS or MSA addresses to MS Mail (PC).
 To implement this configuration
To implement this configuration
Obj-class,common-name,target-address,when-created,display-nameobj-class,mode,common-name,secondary-proxy-addressFollow this procedure every week. Sort first on when-created, and delete all the old entries.
Sample Configuration No. 3 The Microsoft Exchange Server computer connects directly to MS Mail (AppleTalk) and MS Mail (PC) and is a requestor to an MS Mail (PC) postoffice directory synchronization server. Microsoft Exchange Server and MS Mail (PC) have MS addresses for MS Mail (AppleTalk) mailboxes.
 To implement this configuration
To implement this configuration
Obj-class,common-name,target-address,when-createdobj-class,mode,common-name,secondary-proxy-addressFollow this procedure every week. Sort first on when-created, and delete all the old entries.
You should convert gateway recipients in MS Mail (AppleTalk) servers to Microsoft Exchange Server custom recipients. To do this, you use the MS Mail Administrator program to create a list of gateway recipients, and you put this list into directory import format. Import the list to Microsoft Exchange Server using the Administrator program.
For more information about custom recipients, see Microsoft Exchange Server Operations.
Note There must be a corresponding gateway in the organization for which their addresses are valid. You cannot send mail from Microsoft Exchange Server through an MS Mail (AppleTalk) gateway.