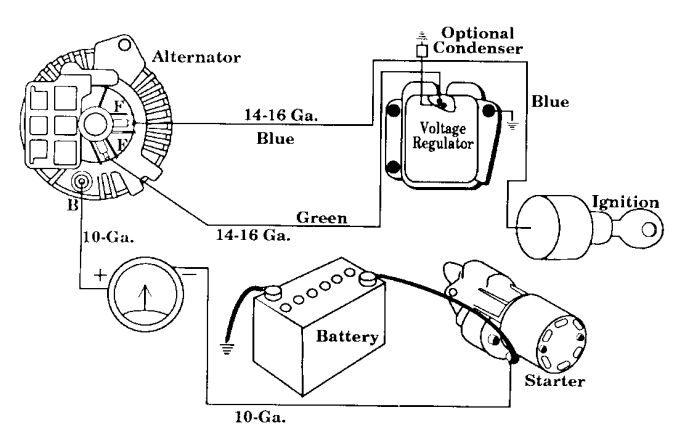
Charging System
CHARGING SYSTEMS
Early vehicles were made with 6 volt electrical systems. Although some were negative earth the standard was in fact positive earth.
The early battery charging systems were D.C. generators with cut out relays. Later models used more sophisticated voltage regulators that regulated both the voltage and the current being supplied to the battery.
In the mid '50s auto. manufacturers switched over to 12 volt systems with a negative earth but still used D.C. generators to replenish the battery.
It was in the early '60s when manufacturers started using alternators. These produce A.C. current which cannot be directly used to recharge a battery without first being "rectified" to convert it to D.C. current. This is normally accomplished using diodes.
The advantage of using an alternator is that it can provide enough voltage to the battery even at idle. A generator needs to be spinning faster than it would at idle to produce a comparable amount of electricity.
An alternator MUST have battery voltage present to produce a magnetic field in the spinning rotor or there is no output. A generator will produce electricity as soon as it starts spinning fast enough. It needs no external voltage to get it operating. This means that if a cars battery is completely flat, and it uses an alternator, then it is impossible to push-start the vehicle.
Voltage regulators are used between the generator/alternator and the battery to provide a constant charging voltage.
Early regulators were mechanical and could be adjusted for output. Chrysler were the first to employ solid state electronic regulators in the late '60s. All of these early types were mounted on the inner fender or bulkhead.
When G.M. switched to electronic regulators they housed them inside the alternator itself. These alternators tend to put out a bit more voltage than their predecessors because they are designed to work with maintenance free batteries which require a higher charging voltage. If you use the old type of battery with one of these alternators you will boil the water out of the acid at a higher rate then would normally be the case.
To test your cars charging system connect a voltmeter across the battery with the engine running. Charging voltage should be approximately 14.4 volts. If the voltmeter reads above 15.0 volts then the charging system is overcharging the battery.
Early vehicles were made with 6 volt electrical systems. Although some were negative earth the standard was in fact positive earth.
The early battery charging systems were D.C. generators with cut out relays. Later models used more sophisticated voltage regulators that regulated both the voltage and the current being supplied to the battery.
In the mid '50s auto. manufacturers switched over to 12 volt systems with a negative earth but still used D.C. generators to replenish the battery.
It was in the early '60s when manufacturers started using alternators. These produce A.C. current which cannot be directly used to recharge a battery without first being "rectified" to convert it to D.C. current. This is normally accomplished using diodes.
The advantage of using an alternator is that it can provide enough voltage to the battery even at idle. A generator needs to be spinning faster than it would at idle to produce a comparable amount of electricity.
An alternator MUST have battery voltage present to produce a magnetic field in the spinning rotor or there is no output. A generator will produce electricity as soon as it starts spinning fast enough. It needs no external voltage to get it operating. This means that if a cars battery is completely flat, and it uses an alternator, then it is impossible to push-start the vehicle.
Voltage regulators are used between the generator/alternator and the battery to provide a constant charging voltage.
Early regulators were mechanical and could be adjusted for output. Chrysler were the first to employ solid state electronic regulators in the late '60s. All of these early types were mounted on the inner fender or bulkhead.
When G.M. switched to electronic regulators they housed them inside the alternator itself. These alternators tend to put out a bit more voltage than their predecessors because they are designed to work with maintenance free batteries which require a higher charging voltage. If you use the old type of battery with one of these alternators you will boil the water out of the acid at a higher rate then would normally be the case.
To test your cars charging system connect a voltmeter across the battery with the engine running. Charging voltage should be approximately 14.4 volts. If the voltmeter reads above 15.0 volts then the charging system is overcharging the battery.